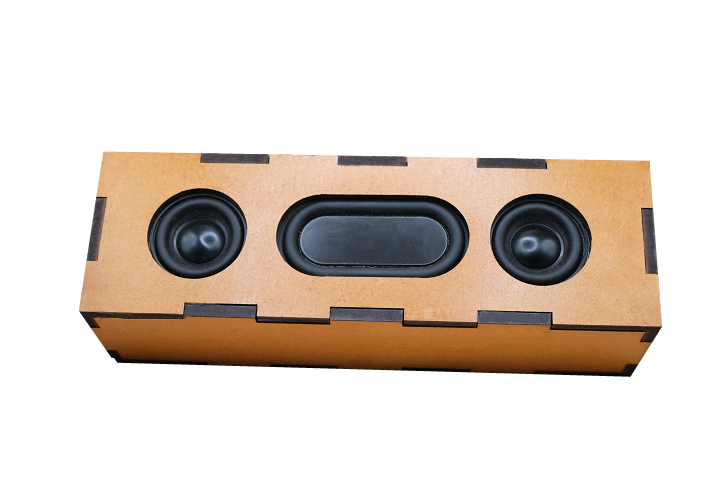
IceTronics Basic Bluetooth speaker kit
$ 42.00
- Spark creativity with STEM education – build a real, working Bluetooth speaker.
- It’s not just a toy; it’s a great learning tool for wireless audio and electronics basics.
- No prior experience needed – the step-by-step guide makes it perfect for beginners and advanced learners.
- The perfect gift for curious minds. It’s great for classrooms, home learning, and hands-on education.
- Professional-grade components with USB-C charging, stereo speakers, and true Bluetooth connectivity.
- Unleash creativity – students create their own custom speaker cases in a style that reflects them.
- Teaches real-world circuits in a device that students actually want to use and show off.
- Safe, portable, and fully functional – take home a speaker you built and use it every day.
Description
The DIY Bluetooth speaker kit makes learning electronics fun and practical. It turns theory into an exciting hands-on project. Students learn about circuits and wireless technology. They build something real.
This kit gives students a complete electronics learning experience. They assemble individual components into a working Bluetooth speaker. They see how wireless audio reception, power management, and sound amplification work together.
The result is both educational and practical. Students gain a true understanding of electronics. They also create a fully functional speaker with their own hands.
Perfect for tech classes, STEM programs or home learning, this kit requires no prior electronics experience. The assembly guide helps students understand each connection. It clearly explains what each part does and why it is important.
What’s Included?
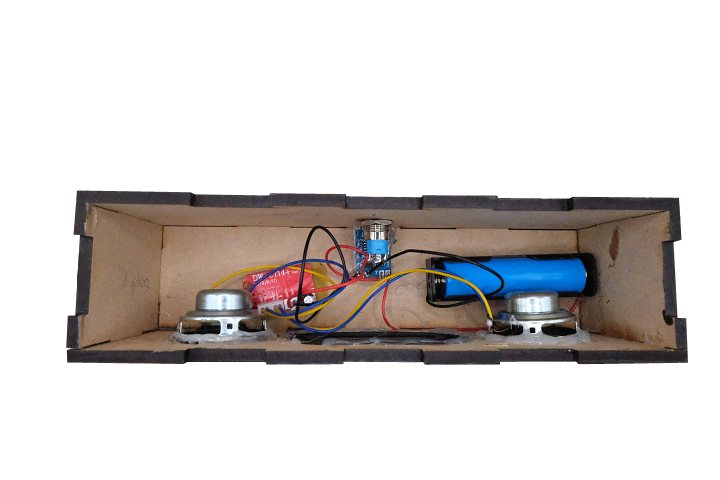
Each kit contains all the electronic components needed to build a complete Bluetooth speaker system:
Audio Components:
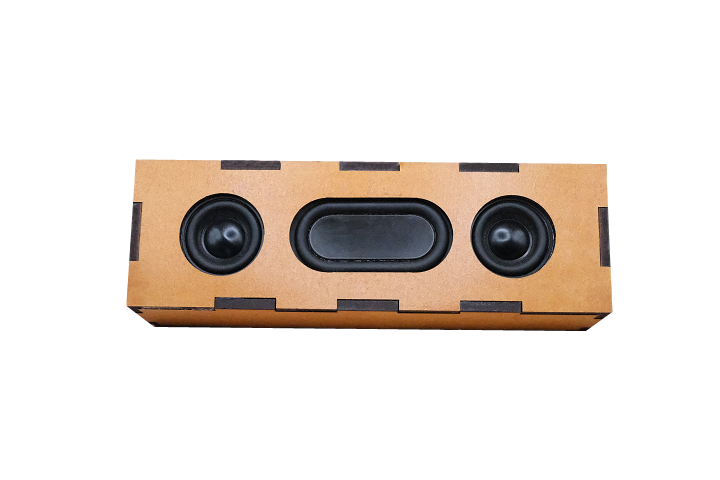
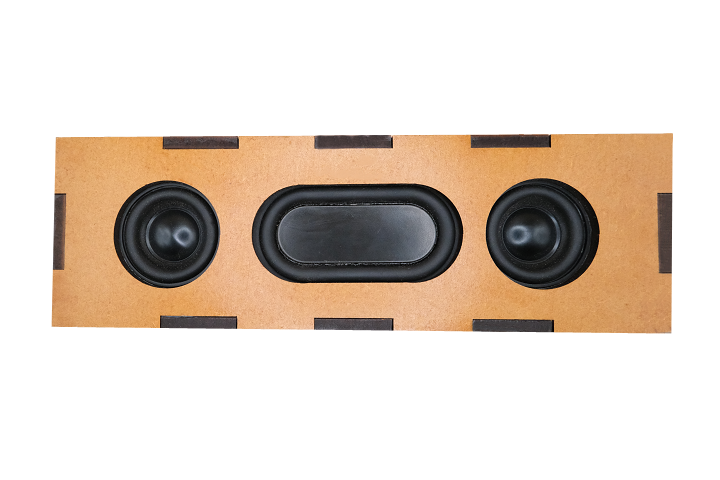
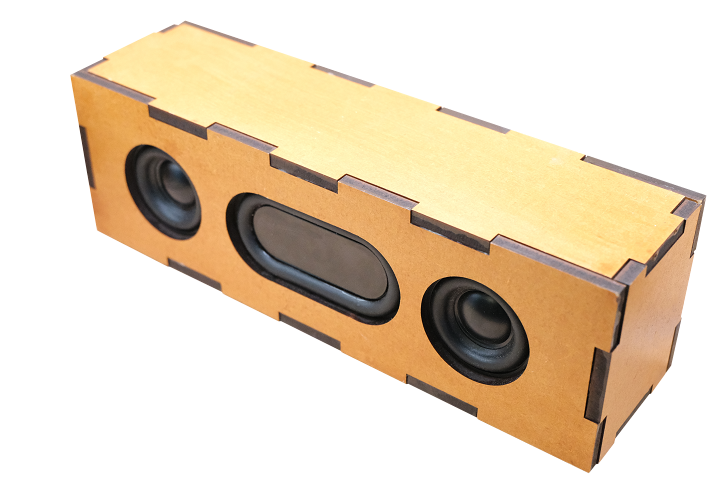
- Two 40mm stereo speakers (4Ω, 5W) for left and right audio channels
- One passive radiator to enhance bass response and sound quality
- Bluetooth amplifier module with wireless audio reception and signal amplification
Power System:
- 3.7V lithium-ion rechargeable battery (18650 type)
- Battery holder for safe, tool-free battery installation
- USB-C battery charging module with built-in safety protection
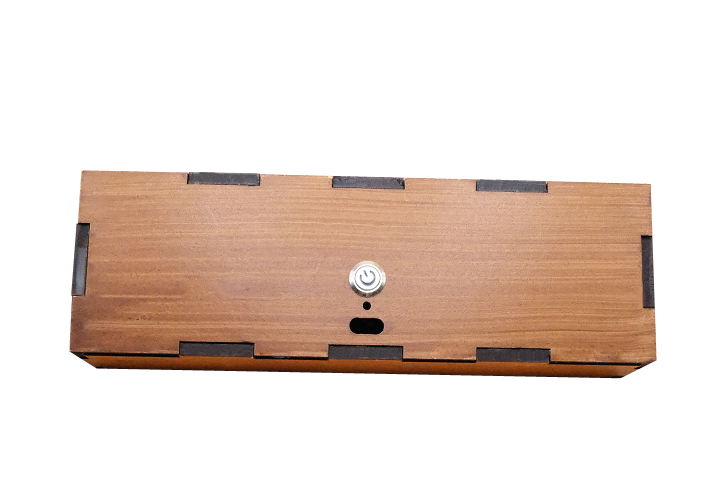
- 12mm latching push-button power switch
Wiring:
- Connection wires (two red, one black, 5cm length)
- Complete wiring diagram showing all connections
Documentation:
- Detailed assembly and wiring guide
- Component explanation with circuit block diagram
- Testing and troubleshooting procedures
Note: Speaker case/enclosure materials are not included. Students design and fabricate their own custom cases using materials of their choice. This allows for creative expression and additional hands-on learning in design and fabrication.
Learning Outcomes and Benefits
Electronics Fundamentals:
Students gain a practical understanding of real electronic circuits. They learn how power moves from the battery to the charging module. Then, it goes to the amplifier. They understand why polarity matters and how incorrect connections can damage components.
The kit introduces key concepts, including voltage regulation, current flow, and circuit protection. Students see these abstract ideas in action as they wire components together.
Wireless Technology:
Students explore how Bluetooth technology works in everyday devices. They learn about wireless audio transmission, signal reception, and digital-to-analog conversion. The amplifier module shows how weak wireless signals can be boosted. This helps drive speakers more effectively.
Audio Engineering Basics:
The kit teaches fundamental audio concepts. Students understand stereo sound with separate left and right channels. They discover how speakers convert electrical signals into sound waves through physical vibrations.
The passive radiator introduces acoustic principles. Students discover how enclosed speakers generate air pressure. They also learn how passive elements improve low-frequency response without needing extra power.
Power Management:
Students work with modern rechargeable battery technology. They learn why lithium-ion batteries need controlled charging. Protection circuits help prevent damage. The USB-C charging module demonstrates current regulation and voltage monitoring.
The power switch teaches basic control circuits. Students learn how switches stop current flow. This helps prevent battery drain when the speaker is off.
Problem-Solving Skills:
Assembly requires careful attention to detail. Students must verify connections, check polarity, and follow sequences correctly. When problems occur during testing, they learn systematic troubleshooting.
This builds analytical thinking. Students learn to trace problems back to their source rather than guess at solutions.
Creative Design Integration:
Beyond electronics, students engage in creative design. They plan their speaker enclosure, considering both aesthetics and acoustics. They choose materials and fabrication methods. They turn functional electronics into personalized products.
This mix of technical skill and creativity makes learning meaningful and memorable.
Real-World Application:
Unlike abstract exercises, this project creates something students actually use. They’re not building a circuit that blinks an LED. They’re building a Bluetooth speaker that plays their music.
This real-world connection makes learning relevant. Students see why these electronic principles matter beyond the classroom.
Product Specifications
Audio Performance:
- Speaker drivers: 40mm diameter, 4Ω impedance, 5W power rating (pair)
- Configuration: Stereo (separate left and right channels)
- Bass enhancement: Passive radiator for improved low-frequency response
- Audio input: Bluetooth wireless connection (compatible with phones, tablets, computers)
Power System:
- Battery type: 18650 lithium-ion rechargeable cell
- Battery voltage: 3.7V nominal
- Charging interface: USB-C connector
- Charging protection: Built-in voltage and current regulation
- Power control: Latching push-button switch with optional LED indicator
Physical Specifications:
- Assembly time: 30 minutes for basic electronics assembly
- Case design/fabrication time: Variable (several hours depending on design complexity)
- Portability: Fully portable with rechargeable battery power
- Weight: Depends on case materials chosen by student
Skill Level:
- No prior electronics experience required
- Suitable for middle school students through adult learners
- Basic soldering skills needed for permanent connections
- Adult supervision recommended for younger students
Safety Features:
- Battery holder prevents direct soldering to battery
- Charging module includes overcharge and overcurrent protection
- Clear polarity markings prevent incorrect connections
- Comprehensive safety warnings in assembly guide
Tools and Materials Required
Tools Needed (Not Included):
Students will need access to these basic electronics tools:
- Soldering iron and solder for making permanent wire connections
- Wire cutters or wire strippers for preparing connection wires
- Small screwdriver (if mounting components to case)
- Multimeter (optional but helpful for troubleshooting)
Materials for Speaker Case (Not Included):
Students design and create their own speaker enclosure using materials of their choice. Common options include:
- Wood (plywood, MDF, solid wood)
- Plastic (3D printing, formed sheet plastic)
- Cardboard or foam board (for quick prototypes)
- Recycled materials (tins, boxes, containers)
Additional materials students may need:
- Adhesive (hot glue, wood glue, super glue depending on materials)
- Mounting hardware (screws, standoffs if desired)
- Finishing materials (paint, stain, fabric covering)
- Acoustic dampening material (optional, for sound quality improvement)
Workspace Requirements:
Students should work in a space with:
- Adequate lighting and ventilation
- Access to electrical outlets (for soldering iron)
- Flat, heat-resistant work surface
- Safe storage for small components during assembly
Charging Requirements:
After assembly, students need:
- USB-C charging cable (standard phone charger type)
- USB power source (computer, wall adapter, power bank)
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q: Do students need prior electronics experience?
No prior experience is required. The assembly guide explains every component in simple terms. Adult supervision is recommended for younger students during soldering.
Q: How long does assembly take?
Electronics assembly takes approximately 30 minutes. Designing and creating the speaker case adds several hours depending on complexity. Students can complete electronics first, then work on the case separately.
Q: What’s the difference between this and a pre-made speaker?
Pre-made speakers hide the electronics inside. This kit shows students every component and connection. They understand the complete system because they built it themselves.
Q: Is soldering required?
Yes, basic soldering is needed for permanent connections. This is an important electronics skill that students learn during the project. Adult supervision is recommended for younger or inexperienced students.
Q: How is the battery charged?
Simply plug in any standard USB-C cable, like a phone charger. The charging module has an LED indicator and built-in protection to prevent overcharging.
Q: Can students customize the speaker?
Absolutely. Students design their own speaker case from scratch, choosing materials, shape, size, and appearance. This makes each project unique and personally meaningful.
Q: What devices can connect to the speaker?
Any Bluetooth-enabled device works—smartphones, tablets, computers, and music players. Pairing is the same as connecting to commercial Bluetooth speakers.
Q: Is this safe for younger students?
The kit includes safety features like battery holders and protection circuits. However, students work with electrical components and soldering equipment. Adult supervision is recommended for middle school students and required for younger children.
Q: What if something doesn’t work after assembly?
The assembly guide includes troubleshooting steps. Most problems come from incorrect polarity or loose connections. This troubleshooting process is a valuable learning experience itself.
Q: How loud is the finished speaker?
The speaker produces clear volume suitable for personal listening or small groups. It’s like small commercial Bluetooth speakers. It’s great for desks, bedrooms, or outdoor use.
Q: Can students reuse components for other projects?
Yes, with careful disassembly. The battery, charging module, and amplifier are all reusable. This extends the educational value beyond the initial build.
Q: What makes this educational versus a DIY project?
Each component teaches a specific concept: power handling, voltage regulation, control circuits, signal processing, and electromechanical conversion. Students understand why each step matters and how components work together.
Q: Is this suitable for classroom use?
Absolutely. The 30-minute assembly time fits standard class periods. Multiple students can work simultaneously with individual kits. Teachers can add lessons on circuit theory or wireless communication to the project.
Note: The design and fabrication of the enclosure will take longer, depending on the efficiency of creating the design and fabricating the case.
Q: What age range is this appropriate for?
The kit works well for middle school through adult learners. Younger students (ages 11–13) benefit from adult guidance during soldering. High school students typically work independently.
You must be logged in to post a review.







Reviews
There are no reviews yet.